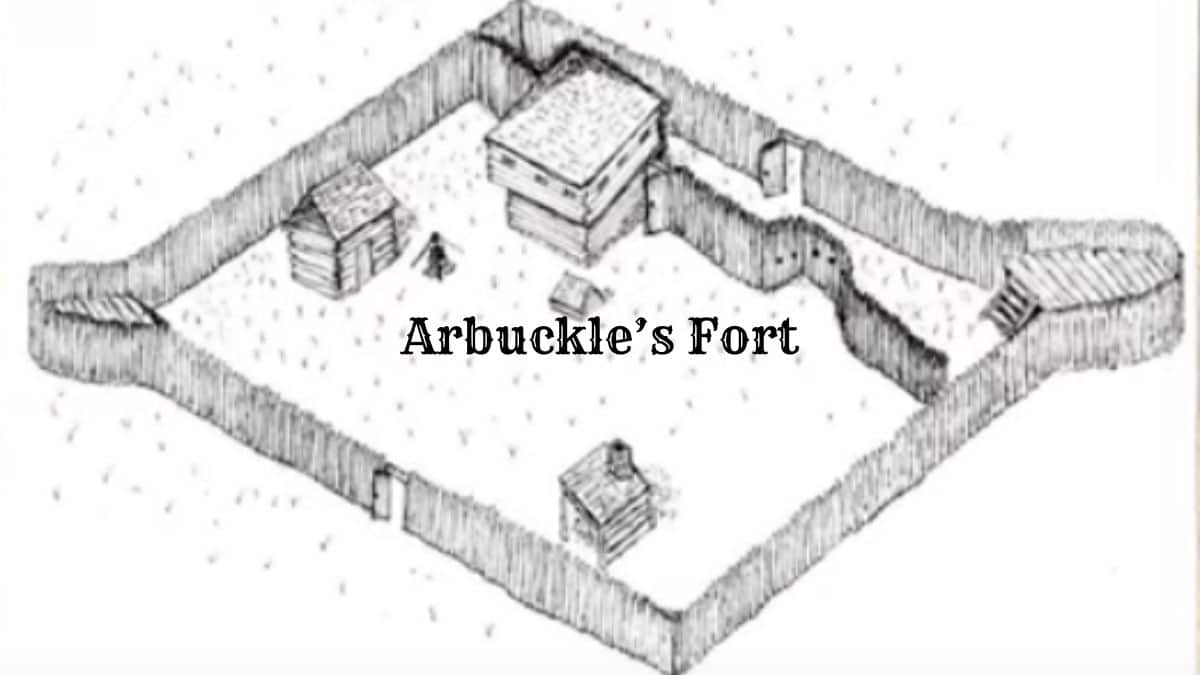
Arbuckle’s Fort, an essential landmark in early American history, offers a unique glimpse into 18th-century frontier defense.
It has fascinated historians and archaeologists in present-day West Virginia for decades. Stephen McBride’s excavations have unearthed significant artifacts, reshaping our understanding of its strategic importance.
The fort’s construction, led by Captain Matthew Arbuckle and his militia, provided critical defense against threats, particularly during the American Revolution.
Today, preservation efforts and ongoing archaeological research ensure that Arbuckle’s Fort remains a vital source of historical insight and a testament to the resilience of early settlers.
Historiography of Arbuckle’s Fort
Arbuckle’s Fort has garnered interest from historians and archaeologists through decades of research.
A notable archaeological figure, Stephen McBride, has led excavations that have revealed much about this historical site. His findings have reshaped perspectives on 18th-century frontier defense.
Historical Documentation: Early documents identified the fort’s location but lacked thorough descriptions. Later, records have been more detailed, contributing to a richer understanding of its strategic importance.
Key Excavations
- Initial Surveys: Early studies focused on identifying fort boundaries.
- 2000s Excavations: Significant digs uncovered remnants of fort structures.
- Recent Finds: Artifacts like musket balls and pottery indicate daily life and defense strategies.
Archaeologists continue to analyze these findings, piecing together the fort’s historical narrative. The Archaeological Conservancy supports their work, ensuring the site’s preservation for future studies.
Founding of the Settlement
The establishment of Arbuckle’s Fort focused on strategic construction and leadership, playing a pivotal role in the defenses of Greenbrier County, Virginia (now West Virginia).
Matthew Arbuckle and his militia company were central to this effort.
Initial Setup and Construction
The initial setup of Arbuckle’s Fort involved the careful planning and construction of robust fortifications.
Positioned strategically in Greenbrier County, the fort featured wooden palisades, blockhouses, and bastions for defense.
Settlers and militia under Captain Matthew Arbuckle’s command worked tirelessly. They constructed a stockade to protect against potential threats.
The fort’s placement was chosen due to its vantage point, overseeing key trails and water sources. This location was essential for the fort’s defensive capabilities.
The main components of the fort included blockhouses that served as lookout points, bastions that strengthened the corners, and a stockade that encircled the settlement.
The combined efforts of the settlers and Arbuckle’s leadership resulted in a formidable structure.
Key Personnel and Leaders
Captain Matthew Arbuckle was the primary leader during the fort’s establishment. His role was pivotal in organizing the construction efforts and the military defense of the settlement.
Arbuckle’s leadership skills and understanding of military fortifications were crucial in developing the fort.
Alongside Arbuckle, Colonel Andrew Lewis also played a significant role.
Lewis, a seasoned military leader, provided strategic guidance and support. The coordination between Arbuckle and Lewis ensured the fort was well-prepared for any threats.
Key personnel included various settlers who contributed their labor and expertise to the fort’s construction. These individuals, though often unnamed, were integral to establishing and maintaining the settlement’s defenses.
Military Engagements
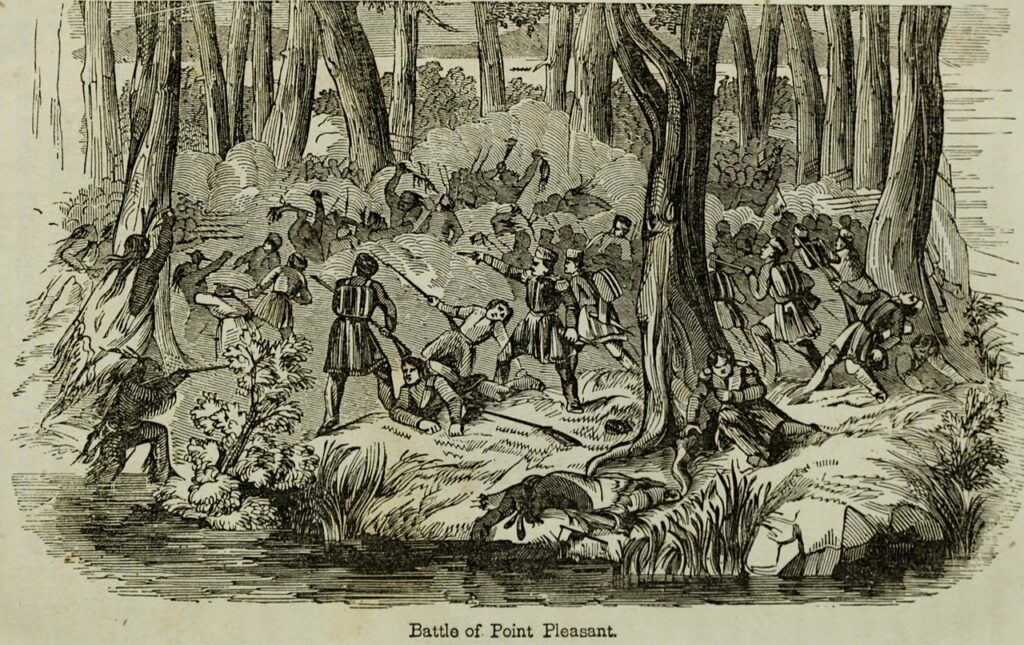

Arbuckle’s Fort played pivotal roles in various military engagements. It was heavily involved during the American Revolution and had numerous interactions and conflicts with Native Americans.
Involvement in the American Revolution
Arbuckle’s Fort was a strategic point for the Virginian militia during the American Revolution. The fort provided a defensive structure against British forces and their allies.
Local militia companies often gathered here to organize their campaigns, including efforts to protect frontier settlements.
During Dunmore’s War, which led up to the revolution, the Battle of Point Pleasant was a significant conflict in which forces from Arbuckle’s Fort participated.
The fort was a staging ground for raids and a haven for troops. The Virginian militia coordinated their defenses effectively despite the numerous threats they faced.
Relations and Conflicts with Native Americans
Arbuckle’s Fort also witnessed numerous conflicts with Native American tribes. The fort was frequently used to repel raiding parties sent by various Indian forces.
These engagements were often brutal and underscored the tense relations between settlers and Native Americans.
The fort’s defenses proved crucial in protecting settlers during these times of conflict.
Moreover, its strategic location allowed for quick responses to threats and facilitated communication with other defensive positions.
These interactions significantly impacted the local dynamics and played a central role in the area’s history.
Architectural Layout and Features
Arbuckle’s Fort showcases a strategic, meticulously planned design with distinctive structural facets. These details underline its importance as a historic military installation.
Fort Design and Structural Elements
The fort’s layout includes a diamond-shaped stockade with prominent bastions at each corner, enhancing its defensive capabilities.
Wooden palisades form the main fortifications, reinforced by post molds indicating their positions.
Central to the structure, the blockhouse offers a fortified position for defense and command.
Archaeological evidence includes refuse-filled pits that provide insights into daily life and fort operations.
Gates monitored the entry points, ensuring controlled access. The stockade’s design reflects its purpose of providing robust protection in a strategic location.
Support Structures and Amenities
Supporting the main defensive structures, Arbuckle’s Fort included essential amenities for sustenance and operational efficiency.
A stone chimney base suggests the presence of a well-built kitchen or heating source.
Storage pits were used for grain, while a powder magazine securely stored gunpowder.
Significant slag concentration points to a blacksmithing area, which is crucial for repairs and weapon manufacturing.
Trenches surrounding the fort provided additional fortification, and evidence of smaller support structures, like a possible Monument or signal posts, enhanced functionality.
The layout ensured the fort could sustain prolonged defenses and maintain operational readiness.
Archaeological Investigations
Archaeological investigations at Arbuckle’s Fort have yielded significant insights into its historical importance.
Key discoveries made during excavations include well-preserved structures and a variety of artifacts, shedding light on daily life in the 18th century.
In addition, the preservation efforts undertaken highlight the ongoing commitment to maintaining the site’s archaeological integrity.
Discoveries at Arbuckle’s Fort
Archaeologists, particularly Stephen McBride and Kim McBride, have led excavations at Arbuckle’s Fort, unearthing several important findings.
These discoveries include remnants of log structures, a unique feature for forts of the period.
Artifacts discovered include pottery fragments, metal tools, and personal items that provide a picture of life at the fort.
The presence of military paraphernalia suggests the fort’s strategic importance.
Archaeologists have also identified defensive earthworks and palisade trenches, proving that Arbuckle’s Fort was a well-planned defensive position.
Preservation of the Site
The Archaeological Conservancy has championed the preservation of Arbuckle’s Fort.
Their efforts ensure the protection and maintenance of the site for future research and public interpretation.
The conservancy’s initiatives involve stabilizing the remains and implementing measures to prevent erosion and other environmental damage.
Public interpretation programs have been vital in educating visitors about the fort’s historical context and archaeological significance.
These programs include guided tours and informational displays that help the public understand the fort’s historical place.
Preservation work also involves continuous research to keep adding to the knowledge base about Arbuckle’s Fort, ensuring its historical story remains intact for generations.
The Fort’s Role in Regional Development
Arbuckle’s Fort played a vital role in the regional development of the Greenbrier Valley. Its strategic location on the Allegheny frontier was crucial for protecting settler communities during the settlement period.
Greenbrier County, with its rich, fertile lands, attracted many settlers. Arbuckle’s Fort provided a secure base for settlers to expand their farms and build new homes.
Key Contributions of Arbuckle’s Fort:
- Safety and Security: The fort offered a defensive stronghold against potential threats, allowing communities to flourish.
- Economic Growth: Protection ensured agricultural activities could thrive, boosting the local economy.
- Community Hub: The fort became a central meeting place, fostering social ties among the settlers.
The presence of Arbuckle’s Fort encouraged further settlement and development in the Greenbrier Valley. With a safe environment, the region saw increased population and prosperity.
Explore More: 11 Historic Forts in West Virginia: An Amazing Historical Insight
Environmental and Strategic Significance
Arbuckle’s Fort was of significant strategic value due to its location and environmental conditions. These factors played essential roles in its defensive capabilities and sustenance.
Geographical Importance of Site Location
The fort was situated on a knoll near the confluence of Muddy Creek and the Greenbrier River. This position gave the fort a vantage point for surveillance of the surrounding area.
Mill Creek also flowed nearby, providing essential water resources. The natural streams around the fort served both sustenance and strategic defense.
The location allowed for easier detection of incoming threats and facilitated communication and transport via the waterways. Its placement at a junction of multiple water sources was crucial in the fort’s defense strategy.
Seasonal and Climate Considerations
The climate around the fort’s location played a significant role across different seasons.
The Fall of 1774 saw frequent skirmishes, and the fort’s design took seasonal changes into account.
Winters could be harsh, requiring robust storage and heating solutions.
Springs provided an abundance of water and renewal of natural resources, giving strategic advantages in terms of supply acquisition.
The summer and fall seasons it facilitated more accessible travel and communication. The seasonal cycle demanded that the fort remain resilient against varied climatic challenges while ensuring the well-being of its inhabitants and defenders.
Cultural and Community Impact
Arbuckle’s Fort has significantly shaped its locality’s cultural dynamics and community engagement. Its preservation has fostered tourism and educational collaboration, enriching public knowledge and local pride.
Tourism and Public Interest
Arbuckle’s Fort Archaeological Site attracts numerous tourists, bolstering the local economy.
Visitors are drawn to its historical significance and the opportunity to explore a well-preserved site.
The West Virginia Encyclopedia and Greenbrier Historical Society have helped raise awareness about the fort’s heritage.
The James Graham House in Alderson and other heritage sites complement the fort, creating a well-rounded historical experience for tourists.
These attractions offer various tourism activities, including guided tours and reenactments, enhancing the visitor experience.
This increase in tourist footfall supports local businesses like restaurants and shops, contributing to the region’s economic vitality.
Educational Contributions and Partnerships
Educational institutions and organizations have formed valuable partnerships to promote learning through Arbuckle’s Fort.
Collaborative efforts with the West Virginia Land Trust and local schools have provided rich educational programs.
These programs include field trips and archaeological digs, offering hands-on learning opportunities for students.
The Greenbrier Historical Society also vitally organizes workshops and seminars, which benefit students and history enthusiasts.
Public interpretation efforts ensure that visitors and locals alike gain a deeper appreciation of the fort’s historical context and significance.
These educational contributions preserve history and inspire future generations to value and protect cultural heritage.
Historical Perspectives and Legacy
Arbuckle’s Fort holds a significant place in the history of Virginia and West Virginia.
Its legacy is remembered through various accounts and commemorations, reflecting the struggles of the early settlers and the military efforts throughout the American Revolution.
Accounts of Early Settlers and Soldiers
Descriptions of life at Arbuckle’s Fort by early settlers and soldiers provide valuable insights into the era.
Settler communities in Virginia and West Virginia faced constant threats from Native American tribes.
These communities relied on the Virginia Militia for protection, making the fort a critical stronghold in the late 1700s.
Records from Greenbrier Valley Ancestors detail the daily routines of both European and African-American settlers.
Stories recount the arduous conditions and the fort’s strategic importance during the American Revolution.
Soldiers stationed at the fort recorded encounters and battles, emphasizing the fort’s role in the Virginia frontier defenses.
Commemorations and Memorials
Efforts to commemorate Arbuckle’s Fort have been consistent throughout the years.
In West Virginia, local history organizations and descendants of the original settlers often hold events to honor the fort’s history.
The e-wv site mentions various monuments erected to celebrate the fort’s legacy.
Monuments and memorials have been placed at the site to reflect its historical importance.
These initiatives include plaques, local ceremonies, and the preservation of artifacts.
The fort’s impact is celebrated as a testament to the resilience and determination of the settlers and soldiers who once inhabited the region.
Contemporary Archaeology and Research
Contemporary research at Arbuckle’s Fort highlights significant developments in excavation techniques and technological advancements that enhance the overall comprehension of the site’s archaeological context.
Current Excavation Projects
Recent excavation projects focus on uncovering previously unexplored areas of Arbuckle’s Fort.
Led by archaeologists like Kim and Stephen McBride, these projects have revealed an array of artifacts, such as pottery shards, tools, and remnants of structures, that provide insight into the daily lives of the fort’s inhabitants.
Each excavation is meticulously documented to maintain archaeological integrity.
Archaeologists prioritize careful excavation methods to preserve artifacts and context.
Collaborative efforts with local historical societies also help integrate new findings into the broader narrative of the region’s history.
Technological Advances in Study
Advancements in archaeological technology have significantly impacted the study of Arbuckle’s Fort.
Techniques such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and 3D imaging allow researchers to map and visualize subsurface features without invasive digging.
These methods enhance the accuracy and efficiency of site analysis.
Additionally, digital tools facilitate the cataloging and analysis of artifacts.
For instance, databases enable quick cross-referencing of items found at Arbuckle’s Fort with those from other sites.
This approach aids in building a comprehensive understanding of the fort’s historical and cultural significance.

Cory is a website owner and content creator who enjoys fishing, history, coin collecting, and sports, among other hobbies. He is a husband and father of four.
Romans 15:4 For whatever was written in former days was written for our instruction, that through endurance and through the encouragement of the Scriptures we might have hope.