Fort Edward Johnson is a notable landmark with a fascinating past.
It was located in Augusta County, Virginia, and served as a vital defensive post during the American Civil War.
This fortification played an essential role in the Shenandoah Valley defenses, contributing to numerous strategic military maneuvers.
Constructed by Confederate forces, Fort Edward Johnson was named after Brigadier General Edward Johnson.
The site highlights military strategy and offers insights into the daily lives of soldiers stationed there.
Visitors can explore the fort’s well-preserved earthworks and gain a deeper appreciation for its historical importance.
Today, Fort Edward Johnson remains a testament to the ingenuity and resilience of the soldiers who built and occupied it.
Its preservation allows people to connect with a crucial period in American history, making it an invaluable educational resource for those interested in Civil War history.
History of Fort Edward Johnson
Fort Edward Johnson played a crucial role during the Civil War, with important aspects including regional control, architectural features, and military actions. These elements help in understanding the fort’s significance in American history.
The Strategic Significance
Fort Edward Johnson, located in Virginia, was vital on the Allegheny Mountain. It controlled the Staunton-to-Parkersburg Turnpike, a critical route for moving troops and supplies.
This position was essential for the Confederate Army of the Northwest to protect Staunton and Augusta County from Union forces.
The fort allowed Confederate forces to monitor and obstruct Union advances in the region.
The difficult terrain further fortified its defensive position, making it crucial for the Confederate defense system in the Western Virginia theater of the Civil War.
Construction and Design
The construction of Fort Edward Johnson began in the early stages of the Civil War.
It was named after Confederate commander Edward “Allegheny” Johnson, who supervised its development.
Built primarily from earthworks and felled timber, the fort utilized the natural terrain to bolster its defenses.
The fort’s design included trenches, artillery positions, and defensive barriers.
These features showcased military engineering tactics to maximize defensive capabilities while utilizing available materials.
The fort’s placement on the mountain ridge provided natural protection and a strategic vantage point over surrounding areas.
Military Engagements
Fort Edward Johnson saw significant military action during the Civil War.
In early 1862, Confederate forces repelled several Union attempts to penetrate the fort’s defenses.
The fort witnessed the confrontation at the Battle of McDowell, a significant engagement where Confederate forces under Stonewall Jackson utilized the fort’s strategic advantage.
Additionally, smaller skirmishes and engagements around the fort continued to emphasize its strategic importance.
These encounters underscored the fort’s role in the Confederate defensive strategy and highlighted the challenging conditions soldiers faced in the rugged terrain of Virginia.
The Role of Fort Edward Johnson in the Civil War

Fort Edward Johnson played a key role in the Confederate strategy during the Civil War, particularly in the Shenandoah Valley.
It greatly influenced defensive operations and contributed to the larger operational scope of the Confederate Army of the Northwest, impacting both local and national tactics.
Defensive Operations
Fort Edward Johnson served as a crucial defensive position for the Confederate troops during the Civil War.
It was positioned strategically in the Shenandoah Valley and acted as a barrier against Federal troops.
The fort’s high elevation allowed for better surveillance of Union Army movements.
Confederate soldiers could anticipate and counter potential advances, making it difficult for Union forces to gain ground.
Control of this fort was vital in maintaining the security of the Shenandoah Valley.
It safeguarded critical supply lines and protected the heartland of the Confederacy.
The fort’s defensive strength played a significant role in delaying Union advances in the region.
Confederate Army of the Northwest
The fort was central to the operations of the Confederate Army of the Northwest, which was under the command of Edward “Allegheny” Johnson.
This army was tasked with defending the Shenandoah Valley and disrupting Union activities.
Edward Johnson’s forces used Fort Edward Johnson as a base for launching counterattacks.
The fort provided shelter and supplies essential for sustaining prolonged engagements against Federal troops.
The location also boosted the morale of Confederate soldiers.
It symbolized their resilience and ability to hold strategic positions.
The fort’s presence allowed the Confederate Army of the Northwest to operate effectively despite being outnumbered and often under-resourced.
Impact on Local and National Tactics
The strategic importance of Fort Edward Johnson extended beyond local engagements.
It influenced national tactics by forcing Union commanders to allocate significant resources to neutralize its threat.
The fort’s defensive capabilities necessitated prolonged campaigns by the Union Army, diverting their focus from other strategic goals.
This diversion bought the Confederacy valuable time to reorganize and fortify other critical areas.
Locally, the fort impacted civilian life and military activities in the Shenandoah Valley.
Its presence disrupted local supply chains and affected the daily lives of residents.
It highlighted the importance of strong defensive positions in military strategy nationally, influencing future tactics in the Civil War.
Key Military Leaders and Figures
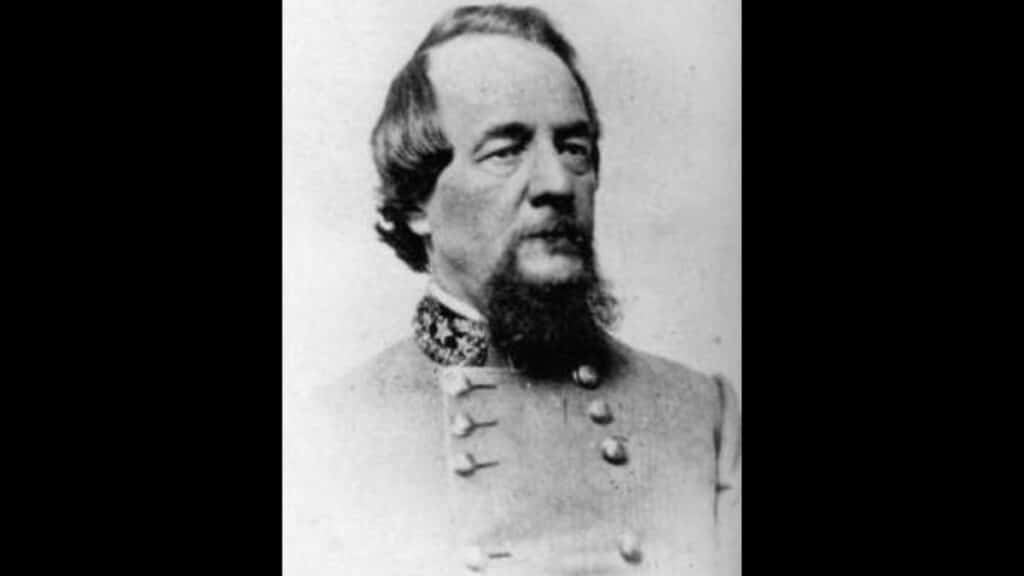

This section addresses significant military leaders such as Colonel Edward ‘Alleghany’ Johnson, his opposition generals, and other influential personalities relevant to Fort Edward Johnson.
Life of Colonel Edward ‘Alleghany’ Johnson
Colonel Edward ‘Alleghany’ Johnson, born in 1816, became a notable Confederate general during the American Civil War.
His military career began in 1838 when he graduated from West Point and served in the U.S. Army.
Johnson earned the nickname ‘Alleghany’ for his defensive stand at the Battle of Alleghany Mountain in 1861. This pivotal battle established his reputation as a determined leader amidst harsh conditions.
Johnson’s role was crucial during the Shenandoah Valley campaigns.
He commanded Confederate forces effectively despite being repeatedly injured.
In 1863, he was promoted to major general, leading troops at significant battles like Gettysburg and Spotsylvania.
His dedication and tenacity contributed substantially to Confederate military efforts.
Opposing Generals
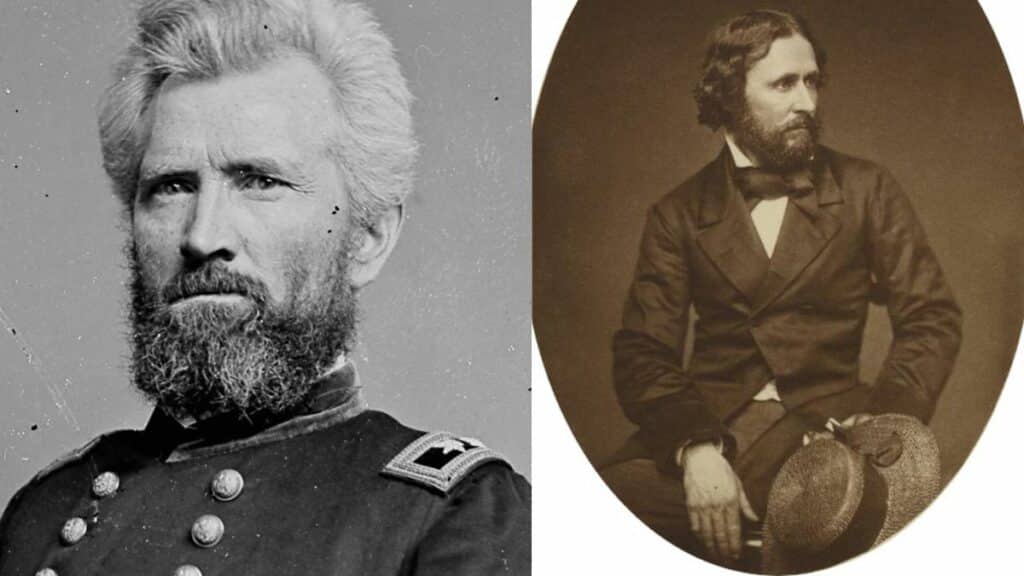

Brig. Gen. Robert H. Milroy, known for his aggressive tactics, opposed Johnson in numerous engagements.
Milroy’s command of Union forces in the Shenandoah Valley led to several confrontations.
His decisive actions in battles such as McDowell in May 1862 demonstrated his willingness to engage the Confederates head-on and reflected his commitment to Union objectives.
Brig. Gen. John C. Fremont also played a critical role.
Appointed to lead the Mountain Department, Fremont’s strategies intersected directly with Johnson’s movements.
Despite friction with superiors, Fremont’s efforts were instrumental in creating pressure on Confederate forces.
His leadership in Western Virginia’s campaigns showcased his resilience and strategic mind in challenging terrain.
Influential Personalities
Several key figures shaped the outcomes of military engagements around Fort Edward Johnson.
Aside from Johnson, the Army of the Shenandoah played a pivotal role.
This Confederate unit, commanded initially by General Joseph E. Johnston and later by others like Johnson, was essential in defending the strategic valley region.
Although less detailed in historical accounts, General Johnson also contributed to the overarching Confederate strategy.
His decision-making and coordination with other commanders influenced the course of multiple battles.
Such cooperation and conflict among leaders highlight the intricate dynamics of Civil War military leadership.
Fort Edward Johnson Today
Today, Fort Edward Johnson is a notable historical site with ongoing preservation efforts, an engaging interpretive trail for visitors, and numerous educational resources that honor its historical significance.
Preservation Efforts
The Fort Edward Johnson site is primarily managed by the U.S. Forest Service, which works to maintain the integrity of this Civil War-era fortification.
Over the years, efforts have been made to protect the structural remnants and surrounding landscape.
Preservation techniques include:
- Regular inspections and maintenance of the earthworks.
- Partnerships with historical societies to support upkeep.
- Grants and funding for conservation activities.
Preservation is crucial to keep the site intact for educational and commemorative purposes. These efforts ensure the fort remains a valuable resource for future generations.
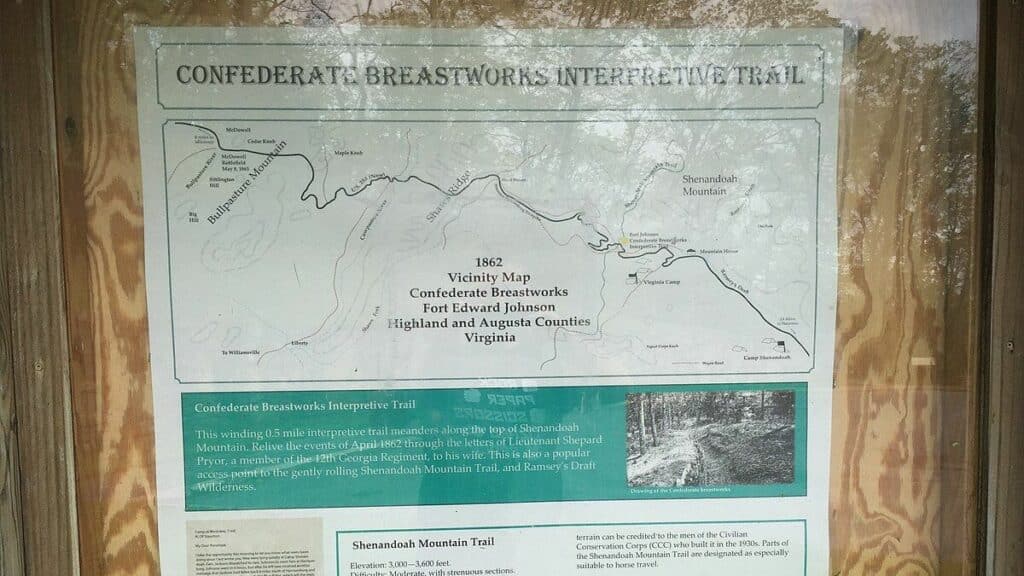
The Interpretive Trail and Tourism
The Confederate Breastworks Interpretive Trail allows visitors to explore Fort Edward Johnson through a well-maintained path.
Located off U.S. 250, this trail provides historical insights and beautiful natural surroundings.
Key features of the trail:
- Informative plaques and markers.
- Guided tours by knowledgeable staff.
- Scenic views that enhance the visitor experience.
Craig Swain’s work in mapping and documenting the area has also contributed to a more engaging and informative trail experience.
This Interpretive Trail attracts tourists annually, boosting local tourism and awareness of the fort’s history.
Educational Resources and Commemoration
Fort Edward Johnson is a valuable educational resource, with numerous programs and materials available for schools, researchers, and history enthusiasts.
Educational initiatives include:
- Historical Marker to provide context about the fort’s role in the Civil War.
- Workshops and seminars conducted by historians.
- Digital archives and publications detailing the site’s history.
Commemorative events, such as reenactments and memorials, are held regularly to honor the fort’s significance.
These activities promote a deeper appreciation of the historical impact of Fort Edward Johnson.
Surrounding Geography

Fort Edward Johnson’s location offers strategic advantages due to its terrain and positioning, aiding defensive and offensive military operations.
Shenandoah Mountain’s Role
The Shenandoah Mountain range is crucial to Fort Edward Johnson’s strategic importance.
The fort is situated on the eastern slopes, providing a commanding view of the Shenandoah Valley.
This vantage point allows for early warning of approaching forces and is a natural barrier against enemy advancements.
The elevation of the Shenandoah Mountains helps in creating a defensible position.
The terrain is difficult for enemy troops to navigate, offering a significant defensive advantage.
Moreover, the dense forest cover in the region provides concealment and protection for stationed forces, contributing to the fort’s security.
Regional Topography and Tactics
The topography surrounding Fort Edward Johnson influences military tactics and strategies.
The fort sits in an area with numerous ridgelines and valleys, ideal for surveillance and ambush tactics.
These ridgelines serve as natural fortifications, making it more challenging for enemy forces to approach unnoticed.
The valleys facilitate troop movements and logistic operations within the region.
They provide protected routes for the transport of supplies and reinforcements.
The combination of ridgelines and valleys creates a dynamic battlefield environment where control of the high ground is crucial.
The specific layout of the terrain impacts artillery placement, offering spots that maximize range and effectiveness.
The area’s natural features are utilized to create layered defenses and complex offensive strategies, enhancing the fort’s overall military value.
Cultural and Historical Interpretation
Fort Edward Johnson, prominent for its role in American history, is interpreted through various markers and literature, preserving its legacy and public memory for future generations.
Markers and Monuments
Markers and monuments at Fort Edward Johnson commemorate events and figures of historical importance. Interpretive signs often highlight its strategic significance during the U.S. Civil War.
The fort is associated with figures like George Washington and influences from the CSA.
Visitors can engage with plaques that detail troop movements, battles fought, and the architectural prowess of the fortification. These markers are vital in educating the public and maintaining the historical narrative.
Literature and Public Memory
Fort Edward Johnson is well preserved in various books, articles, and academic research. Literature serves as a bridge, connecting modern readers with the events and individuals that shaped the fort’s history.
Resources like Fortwiki provide detailed accounts, making the fort’s narrative accessible.
Reenactments and educational programs that bring history to life also shape public memory, ensuring that the stories and lessons from Fort Edward Johnson remain relevant.
Architectural and Military Aspects
Fort Edward Johnson highlights unique fortifications and intricate military designs. These elements serve as critical defenses, characterized by earthworks and trench systems.
Fortifications and Earthworks
Fort Edward Johnson features robust fortifications.
These include substantial earthworks built to protect against artillery and infantry attacks.
The fort’s walls were constructed using mounded earth and wooden revetments, which absorbed and deflected enemy fire. Ditches and berms surrounded the fort, adding layers of protection.
These fortifications were designed to withstand prolonged sieges.
The careful design of ramparts and parapets provided defenders with cover and strategic vantage points.
Soldiers could move along protected paths, ensuring maximum defense with minimal exposure.
This combination of earth and wood made structures durable and relatively quick to construct.
Trench Warfare and Breastworks Design
Trench warfare at Fort Edward Johnson utilized extensive trench systems that connected various defensive positions. These trenches allowed for secure movement between different sections of the fort.
Breastworks, low defensive walls made of earth, wood, or stone, were integral to these trench designs.
Military breastworks offered protection, enabling soldiers to fire upon attackers from a fortified position. The Confederate Breastworks Trail showcases these historical defense lines and highlights their strategic importance.
The design of these works often included zigzag patterns to minimize damage from direct fire.
Trench and breastwork systems balanced defensive strength with the need for mobility and flexibility.
Both elements were crucial in maintaining the fort’s defense during engagements, showcasing a blend of practicality and effective military engineering.
Explore More: 10 Historic Forts in Virginia: An Epic Journey
Infrastructure and Transportation
Fort Edward Johnson’s location was pivotal in its historical significance, especially considering its connections to major routes and transportation developments.
Staunton and Parkersburg Turnpike
The Staunton and Parkersburg Turnpike was a critical route during the Civil War. It facilitated the movement of troops and supplies and linked major battlefields and strategic locations.
Originating from Staunton, Virginia, and stretching to Parkersburg, West Virginia, this turnpike helped connect the Shenandoah Valley with the Ohio River, making it a vital arterial route for commerce and military campaigns.
This turnpike directly influenced Fort Edward Johnson by improving accessibility and logistics. The fort’s location along this route could serve as a defensive point.
Its proximity to this significant transportation corridor provided a logistical advantage.
Modern Accessibility and Routes
Today, Fort Edward Johnson is accessible via modern routes such as U.S. 250. The existing infrastructure ensures easy access for visitors and historians interested in exploring the site.
Route 250, in particular, provides a direct link from Staunton across the Appalachian Mountains. This route continues to support local travel and commerce, mirroring the historical importance of the Staunton and Parkersburg Turnpike.
A designated Parking Area near the fort facilitates visitor access. This modern infrastructure ensures that the historical site remains connected and accessible.
The maintenance of these routes underscores the enduring significance of Fort Edward Johnson in the region’s transportation network.

Cory is a website owner and content creator who enjoys fishing, history, coin collecting, and sports, among other hobbies. He is a husband and father of four.
Romans 15:4 For whatever was written in former days was written for our instruction, that through endurance and through the encouragement of the Scriptures we might have hope.

